With GPS-enabled technology, farmers can easily tag and track their crops, livestock, and equipment with just a few clicks. This revolutionary method has transformed the farming industry by enhancing its efficiency and productivity. The use of Geo Tagging in Agriculture is not only vital for precision farming but also provides a wealth of benefits that we will explore in this blog post. From reducing waste to increasing yields, Geo Tagging is revolutionizing how farmers grow food sustainably while meeting growing food demands.
What is Geo-Tagging?
Geotagging is the process of adding geographical identification metadata to various types of media, such as photos, videos, or text data, using GPS or other location data. The geographical metadata typically includes latitude and longitude coordinates, which can be used to pinpoint the exact location where the media was captured or created. Geotagging can be useful in a variety of contexts, such as social media, travel, photography, and agriculture, among others, as it can provide additional context, enhance discoverability, and improve precision in various applications.
How Geo Tagging is Used in Agriculture
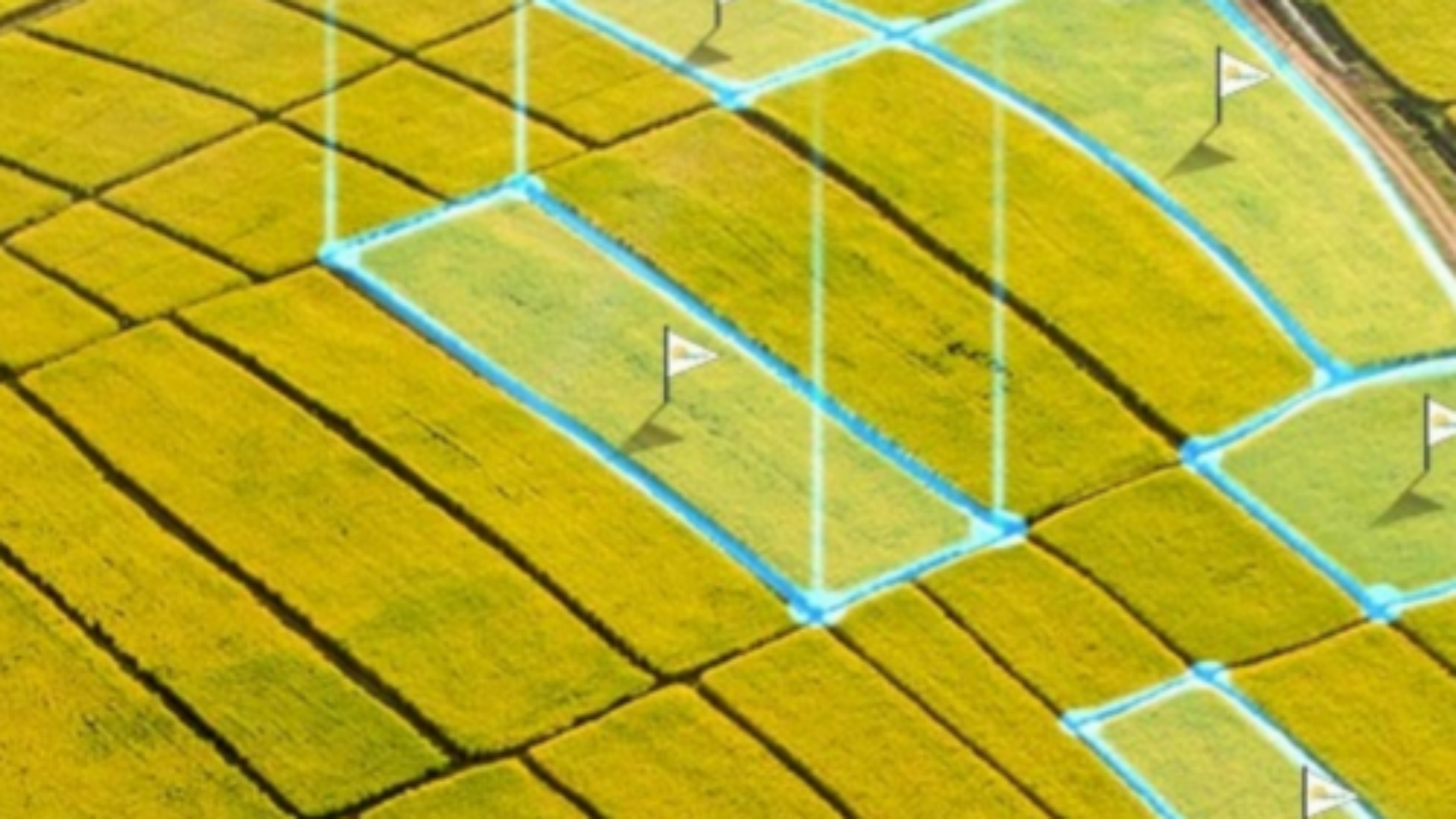
In agriculture, geo-tagging has become an essential tool for farmers and producers to enhance their practices and increase productivity. Farmers use GPS-enabled devices to tag locations on their farms with specific data such as soil type, crop density, and nutrient levels. This enables them to track changes in the land over time and identify areas that require attention or improvement.
Geo-tagging also plays a vital role in supply chain management by enabling traceability from farm to table. By marking products with their origin location, farmers can ensure food safety compliance standards are met while enhancing transparency throughout the entire supply chain.
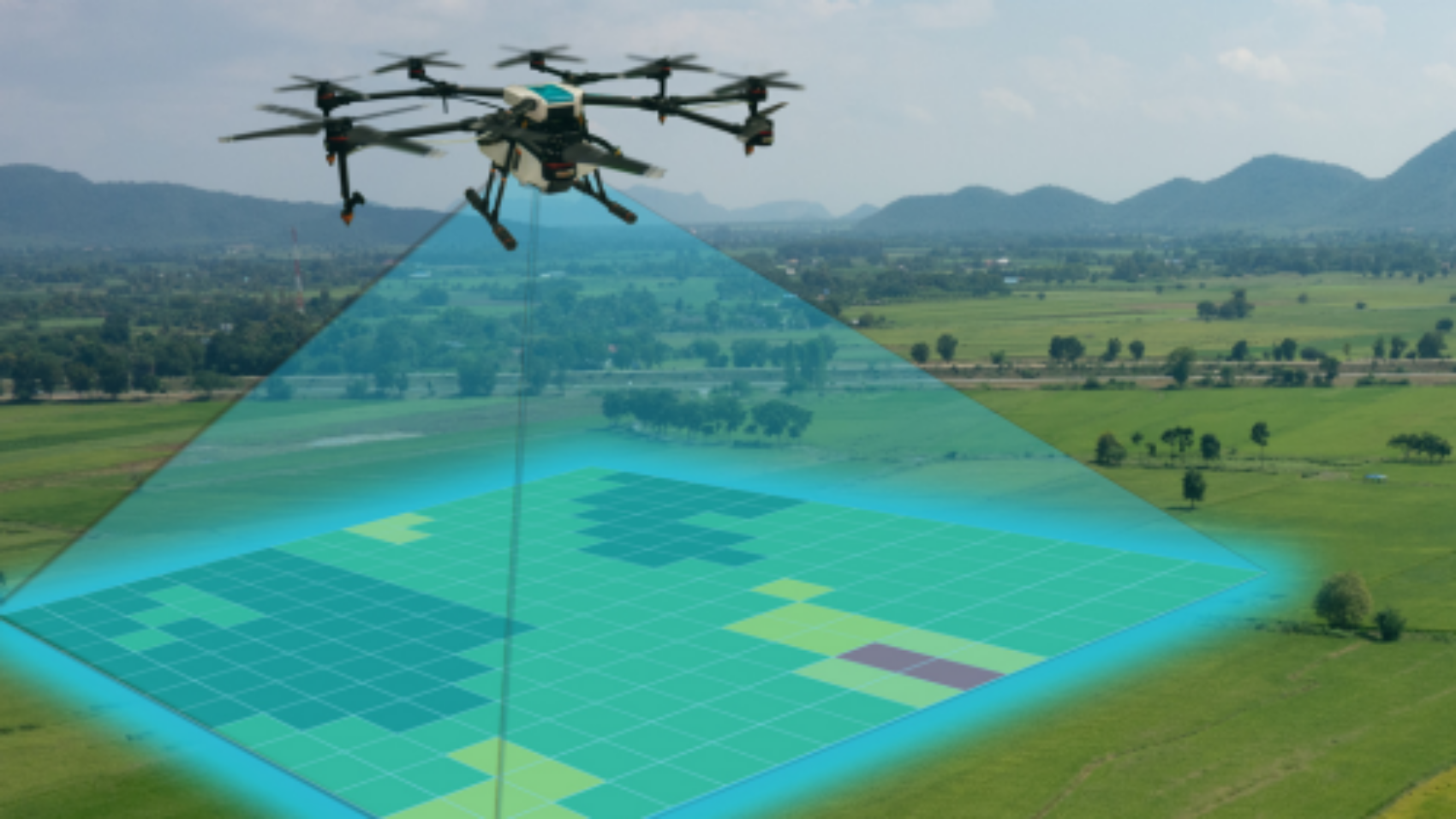
Another way geotagging is used in agriculture is through precision farming techniques. With precise mapping of fields using GPS technology, farmers can accurately apply fertilizers and pesticides where they’re needed most – reducing waste while maximizing yields.
It has revolutionized the agricultural industry by providing valuable information about crops and production processes at every stage from planting seeds to final harvests – driving sustainability efforts forward while improving efficiencies across the board
The Benefits of Geo Tagging in Agriculture
- Improved precision farming: Geotagging can help farmers and agricultural researchers map and analyze crop yields, soil characteristics, and weather patterns in specific locations, allowing for more precise and efficient farming practices.
- Accurate record-keeping: Geotagging can help farmers keep accurate records of where crops were grown and harvested, which can be important for regulatory compliance, food safety, and traceability.
- Better crop management: Geotagging can help farmers identify areas of their fields that may need more or less water, fertilizer, or other inputs, allowing them to optimize crop yields and reduce waste.
- Monitoring crop health: Geotagging can help farmers monitor the health of their crops, by mapping areas of the field where disease, pests, or other issues are present, allowing them to take corrective action more quickly and effectively.
- Enhanced farm-to-market traceability: Geotagging can help trace the movement of crops from the farm to the market, improving food safety and transparency.
Case Study: The Use of Geo-Tagging in Agricultural Production
A case study conducted by a group of researchers at Iowa State University demonstrated how GPS-enabled farm tagging could optimize crop yield.
The research team utilized advanced geospatial technologies to map out the distribution and characteristics of soil types, water availability, nutrient levels, and other environmental factors that influence plant growth. This information was then used to develop precise planting maps for different crops.
By using these maps as a guide during planting, farmers were able to optimize seed placement and ensure that each plant received optimal amounts of nutrients and water throughout the growing season. As a result, crop yields increased significantly compared to traditional farming methods.
Moreover, geo-tagging also helped reduce waste by minimizing over-fertilization or undernourishment in specific areas where it wasn’t necessary. The technology allowed farmers to apply fertilizers more precisely based on soil needs rather than applying them uniformly across an entire field.
Conclusion
Geo-tagging has revolutionized the agricultural industry by providing farmers with an efficient and effective way to manage their crops. GPS-enabled devices have made it possible for farmers to track their farm activities, monitor crop growth, and detect any issues that may arise.
The benefits of Geo Tagging in agriculture are numerous. It helps farmers make informed decisions about when and where to apply fertilizers or pesticides, which ultimately reduces costs while improving yield quality. With the use of geo-tagged images and videos, they can also document the progress of their farming operations.
Moreover, accurate information provided by Geo Tagging technology on soil moisture levels, climate conditions as well as pest infestations on a particular land area at any given time assist in making smart management decisions that help boost productivity.
By embracing Geo Tagging technology in Agriculture production systems worldwide; there is no doubt that this innovative approach will continue transforming global food security through higher yields per acreage cultivated areas amidst environmental challenges posed by climate change uncertainties such as droughts or floods.